Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the Oracle function-based index to speed up queries that consist of functions.
Introduction to Oracle function-based index
We will use the members table created in the CREATE INDEX tutorial for the demonstration.
The following statement creates an index on the last_name column of the members table:
CREATE INDEX members_last_name_i
ON members(last_name);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)If you use the last name column in the WHERE clause, the query optimizer will definitely use the index:
SELECT * FROM members
WHERE last_name = 'Sans';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)However, if you use a function on the indexed column last_name as follows, the query optimizer could not leverage the index:
SELECT * FROM members
WHERE UPPER(last_name) = 'SANS';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following statements show the execution plan of the query above:
EXPLAIN PLAN FOR
SELECT * FROM members
WHERE UPPER(last_name) = 'SANS';
SELECT
PLAN_TABLE_OUTPUT
FROM
TABLE(DBMS_XPLAN.DISPLAY());Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the execution plan:
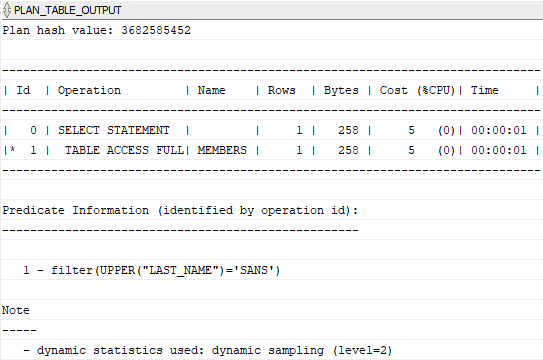
To encounter this, Oracle introduced function-based indexes.
A function-based index calculates the result of a function that involves one or more columns and stores that result in the index.
The following shows the syntax of creating a function-based index:
CREATE INDEX index_name
ON table_name (expression);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax, the index expression can be an arithmetic expression or an expression that contains a function such as a SQL function, PL/SQL function, and package function.
Note that a function-based index can be a btree or bitmap index.
Oracle function-based index example
The following statement creates a function-based index based on the UPPER function:
CREATE INDEX members_last_name_fi
ON members(UPPER(last_name));Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this example, Oracle converted all values in the last_name column to uppercase and stored these results in the members_last_name_fi index.
Now, if you find members by the last name, the query optimizer will consider the index as shown in the following query plan:
EXPLAIN PLAN FOR
SELECT * FROM members
WHERE UPPER(last_name) = 'SANS';
SELECT
PLAN_TABLE_OUTPUT
FROM
TABLE(DBMS_XPLAN.DISPLAY());
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following picture shows the execution plan:
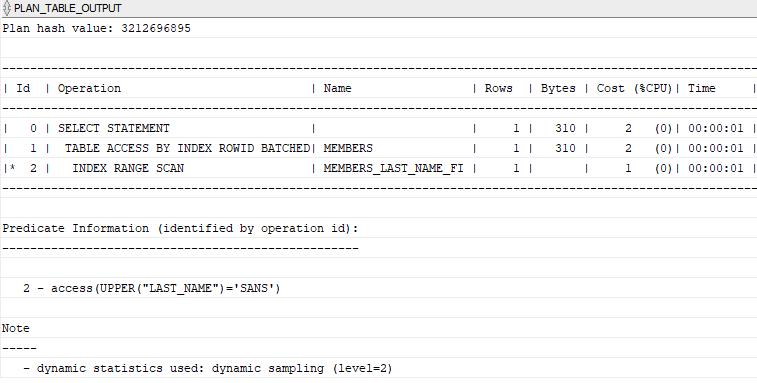
Advantages of function-based indexes
A function-based index has the following main advantages:
- A function-based index speeds up the query by giving the optimizer more chance to perform an index range scan instead of a full index scan. Note that an index range scan has a fast response time when the WHERE clause returns fewer than 15% of the rows of a large table.
- A function-based index reduces computation for the database. If you have a query that consists of an expression and use this query many times, the database has to calculate the expression each time you execute the query. To avoid these computations, you can create a function-based index that has the exact expression.
- A function-based index helps you perform more flexible sorts. For example, the index expression can call
UPPER()andLOWER()functions for case-insensitive sorts orNLSSORT()function for linguistic-based sorts.
Disadvantages of function-based indexes
The following are the major disadvantages of function-based indexes:
- The database has to compute the result of the index in every data modification which imposes a performance penalty for every write.
- The function invoked in the index expression must be deterministic. It means that for the same input, the function always returns the same result.
- The query optimizer can use a function-based index for cost-based optimization, not for rule-based optimization. Therefore, it does not use a function-based index until you analyze the index itself by invoking either
DBMS_STATS.GATHER_TABLE_STATSorDBMS_STATS.GATHER_SCHEMA_STATS.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the Oracle function-based index to speed up queries that involve functions.