Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the Oracle HAVING clause to filter groups returned by the GROUP BY clause.
Introduction to the Oracle HAVING clause
The HAVING clause is an optional clause of the SELECT statement. It is used to filter groups of rows returned by the GROUP BY clause. This is why the HAVING clause is usually used with the GROUP BY clause.
The following illustrates the syntax of the Oracle HAVING clause:
SELECT
column_list
FROM
T
GROUP BY
c1
HAVING
group_condition;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this statement, the HAVING clause appears immediately after the GROUP BY clause.
If you use the HAVING clause without the GROUP BY clause, the HAVING clause works like the WHERE clause.
Note that the HAVING clause filters groups of rows while the WHERE clause filters rows. This is the main difference between the HAVING and WHERE clauses.
Oracle HAVING clause example
We will use the order_items in the sample database for the demonstration.

A) Simple Oracle HAVING example
The following statement uses the GROUP BY clause to retrieve the orders and their values from the order_items table:
SELECT
order_id,
SUM( unit_price * quantity ) order_value
FROM
order_items
GROUP BY
order_id
ORDER BY
order_value DESC;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the result:
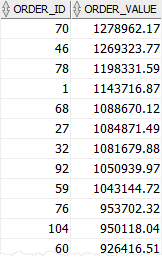
To find the orders whose values are greater than 1 million, you add a HAVING clause as follows:
SELECT
order_id,
SUM( unit_price * quantity ) order_value
FROM
order_items
GROUP BY
order_id
HAVING
SUM( unit_price * quantity ) > 1000000
ORDER BY
order_value DESC;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The result is:
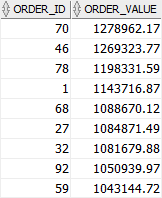
In this example:
- First, the
GROUP BYclause groups orders by their ids and calculates the order values using theSUM() - Then, the
HAVINGclause filters all orders whose values are less than or equal to1,000,000.
B) Oracle HAVING with complex conditions example
You can use a complex filter condition in the HAVING clause to filter groups.
For example, the following statement finds orders whose values are greater than 500,000 and the number of products in each order is between 10 and 12:
SELECT
order_id,
COUNT( item_id ) item_count,
SUM( unit_price * quantity ) total
FROM
order_items
GROUP BY
order_id
HAVING
SUM( unit_price * quantity ) > 500000 AND
COUNT( item_id ) BETWEEN 10 AND 12
ORDER BY
total DESC,
item_count DESC;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the result:
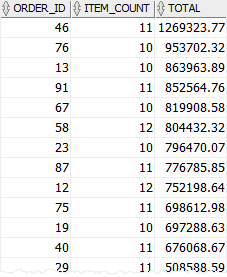
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the Oracle HAVING clause to filter groups of rows returned by the GROUP BY clause.