Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the Oracle TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE data type to store date and time data that includes time zones.
Introduction to Oracle TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE
The TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE data type stores both the time stamp and time zone data.
The time zone data can be time zone offset e.g., -07:00 which is a difference between local time and UTC time, or time zone region name e.g.,Europe/London
The following expression specifies the TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE data type:
TIMESTAMP [(fractional_seconds_precision)] WITH TIME ZONE Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)This expression, fractional_seconds_precision is an optional argument that specifies the number of digits in the fractional part of the SECOND field.
The fractional_seconds_precision ranges from 0 to 9. Its default value is 6.
Oracle considers two TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE values to be equal if they represent the same value in UTC regardless of the time zone data.
For example, the following TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE values are equal:
TIMESTAMP '2017-08-09 07:00:00 -7:00'
TIMESTAMP '2017-08-09 09:00:00 -5:00'Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following statement proves this:
SELECT
DECODE( TIMESTAMP '1999-01-15 8:00:00 -8:00',
TIMESTAMP '1999-01-15 11:00:00 -5:00',
'Equal',
'Not Equal' )
FROM
dual;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Noted that the DECODE() function returns the third argument if the first second equals the second argument, otherwise, it returns the fourth argument.
It is a good practice to use the TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE data type for the application that stores across time zones e.g., event scheduling, banking, and booking applications, etc.
TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE literals
The following format specifies a TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE literal:
TIMESTAMP 'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS.FF TZH:TZM'
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)For example:
TIMESTAMP '2017-08-10 10:30:20.15 -07:00'
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Besides the time zone offset, you can use the time zone region name as follows:
TIMESTAMP 'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS.FF TZR'Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)For example:
TIMESTAMP '2017-08-10 10:30:20.15 US/Pacific'Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)For some regions that have Daylight Saving Time and Standard Time, you should include the TZD format element explicitly to avoid the ambiguity of boundary when the time switches from one to another.
For example, PST for US/Pacific standard time and PDT for US/Pacific daylight saving time. The following value ensures that the Daylight Saving Time value is returned:
TIMESTAMP '2017-08-10 10:30:20.15 US/Pacific PDT'
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)If you don’t specify PDT, Oracle interprets it as the Standard Time if the ERROR_ON_OVERLAP_TIME session parameter is set to FALSE by default or issues an error if ERROR_ON_OVERLAP_TIME is set to TRUE.
The default format for TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE value
By default, the date format for TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE data type is controlled by the NLS_TIMESTAMP_TZ_FORMAT parameter.
SELECT
value
FROM
V$NLS_PARAMETERS
WHERE
parameter = 'NLS_TIMESTAMP_TZ_FORMAT';
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The default value in the Oracle Database is:
DD-MON-RR HH.MI.SSXFF AM TZR
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)If you want to change this default format, you use the ALTER SESSION SET statement.
ALTER SESSION SET NLS_TIMESTAMP_TZ_FORMAT = 'format';
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Please see the Oracle date format for detailed information on how to construct a date format model.
Oracle TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE example
Let’s create a new table named logs for the demonstration.
CREATE TABLE logs
(
log_id NUMBER GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY,
log_message VARCHAR2(255) NOT NULL,
created_at TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(log_id)
);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The data type of the created_at column is TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE. Next, we will show you various ways to insert data into this column.
First, let’s check the session time zone:
SELECT SESSIONTIMEZONE FROM dual;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Currently, it is set to:
-07:00Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following statement inserts a TIMESTAMP value into the created_at column.
INSERT INTO logs(log_message, created_at)
VALUES('Insert a timestamp',TIMESTAMP '2017-08-08 2:00:00');Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Because the time stamp value does not have time zone data, Oracle appended the session time zone before storing it.
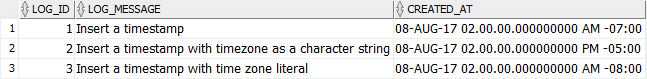
SELECT * FROM logs;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
The following statement inserts a date time in character string format into the created_at column
INSERT INTO logs(log_message, created_at)
VALUES('Insert a timestamp with timezone as a character string','08-AUG-2017 2:00:00 PM -05:00');
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this case, Oracle converted the character string to the corresponding TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE value.
See the following value inserted into the table:

The following statement inserts a TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE literal into the created_at column:
INSERT INTO logs(log_message, created_at)
VALUES('Insert a timestamp with time zone literal',TIMESTAMP '2017-08-08 2:00:00 -08:00');
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is how the data is stored in the table:
The following statement uses the result of the CURRENT_TIMESTAMP function for inserting:
INSERT INTO logs(log_message, created_at)
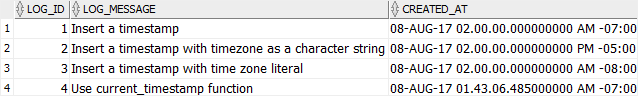
VALUES('Use current_timestamp function',CURRENT_TIMESTAMP);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Oracle inserted the current time stamp with the session time zone into the table:
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the Oracle TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE data type for storing date and time data that includes time zones.