Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the Oracle BETWEEN operator to select rows whose values are in a specified range.
Introduction to Oracle BETWEEN operator
The BETWEEN operator allows you to specify a range to test. When you use the BETWEEN operator to form a search condition for rows returned by a SELECT statement, only rows whose values are in the specified range are returned.
The following illustrates the syntax of the BETWEEN operator:
expression [ NOT ] BETWEEN low AND highCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax:
A) low and high
The low and high specify the lower and upper values of the range to test. The low and high values can be literals or expressions.
B) expression
is the expression to test for in the range defined by low and high. To be able to compare, the data types of expression, low, and high must be the same.
C) AND operator
The AND operator acts as a placeholder to separate between low and high.
The BETWEEN operator returns true if the value of expression is greater than or equal (>=) to low and less than or equal to high.
value >= low AND value <= highCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The NOT BETWEEN operator negates the result of the BETWEEN operator.
The BETWEEN operator is often used in the WHERE clause of the SELECT, DELETE, and UPDATE statement.
Oracle BETWEEN operator examples
Let’s look at some examples of using the Oracle BETWEEN operator.
A) Oracle BETWEEN numeric values example
See the following products table in the sample database:

The following statement returns products whose standard costs are between 500 and 600:
SELECT
product_name,
standard_cost
FROM
products
WHERE
standard_cost BETWEEN 500 AND 600
ORDER BY
standard_cost;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this example, we compared the values in the standard cost ( standard_cost) column with a range from 500 to 600. The query returned only products whose standard costs are between that range:
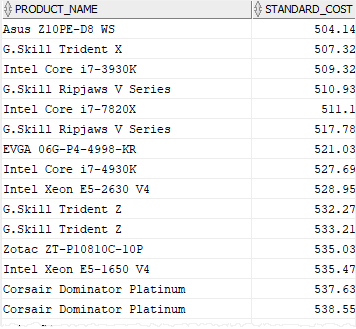
To query products whose standard costs are not between 500 and 600, you add the NOT operator to the above query as follows:
SELECT
product_name,
standard_cost
FROM
products
WHERE
standard_cost NOT BETWEEN 500 AND 600
ORDER BY
product_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following illustrates the result:
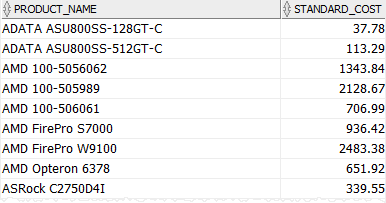
B) Oracle BETWEEN dates example
Let’s use the orders table in the sample database for the demonstration:

The following statement returns the orders placed by customers between December 1, 2016, and December 31, 2016:
SELECT
order_id,
customer_id,
status,
order_date
FROM
orders
WHERE
order_date BETWEEN DATE '2016-12-01' AND DATE '2016-12-31'
ORDER BY
order_date;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the result:
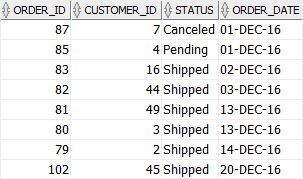
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the Oracle BETWEEN operator to select rows that are in a specific range.