Summary: this tutorial introduces you to the Oracle NVARCHAR2 data type and explains the differences between NVARCHAR2 and VARCHAR2.
Introduction to Oracle NVARCHAR2 data type
The NVARCHAR2 is a Unicode data type that can store Unicode characters. The character set of the NVARCHAR2 is national character set specified at the database creation time.
To find the character set of the NVARCHAR2 in your database, you use the following query:
SELECT
*
FROM
nls_database_parameters
WHERE
PARAMETER = 'NLS_NCHAR_CHARACTERSET';
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)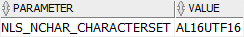
In our Oracle database server, the NVARCHAR2 data type uses AL16UTF16 character set which encodes Unicode data in the UTF-16 encoding. The AL16UTF16 use 2 bytes to store a character.
The NVARCHAR2 stores variable-length character data. When you create a table with the NVARCHAR2 column, the maximum size is always in character length semantics, which is also the default and only length semantics for the NVARCHAR2 data type.
Oracle NVARCHAR2 examples
The following statement creates a table with an NVARCHAR2 column whose maximum length is 50 characters.
CREATE TABLE nvarchar2_demo (
description NVARCHAR2(50)
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Because the current national character set is UTF-16, the maximum byte length of the description column is 200 bytes.
Note that the maximum byte length is the product of the maximum character length and the maximum number of bytes in each character.
The following statement inserts a row into the nvarchar2_demo table:
INSERT INTO nvarchar2_demo
VALUES('ABCDE');Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)We use the DUMP()nvarchar2_demo table:
SELECT
description,
DUMP(description,1016)
FROM
nvarchar2_demo;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
As shown in the result, the datatype code 1 is and the length is 10 bytes (5 characters, 2 bytes each).
VARCHAR2 vs. NVARCHAR2
First, the maximum size of VARCHAR2 can be in either bytes or characters, whereas the maximum size of NVARCHAR2 is only in characters. In addition, the maximum byte length of an NVARCHAR2 depends on the configured national character set.
Second, a VARCHAR2 column only can store characters in the default character set while the NVARCHAR2 can store virtually any characters
The following query returns the default character set used by the VARCHAR2 data type.
SELECT
*
FROM
nls_database_parameters
WHERE
parameter = 'NLS_CHARACTERSET';
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)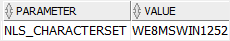
In this tutorial, you have learned about Oracle NVARCHAR2 and the differences between NVARCHAR2 and VARCHAR2.