Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the Oracle INSERT INTO SELECT statement to insert data into a table from the result of SELECT statement.
Overview of Oracle INSERT INTO SELECT statement
Sometimes, you want to select data from a table and insert it into another table. To do it, you use the Oracle INSERT INTO SELECT statement as follows:
INSERT INTO target_table (col1, col2, col3)
SELECT col1,
col2,
col3
FROM source_table
WHERE condition;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The Oracle INSERT INTO SELECTstatement requires the data type of the source and target tables to match.
If you want to copy all rows from the source table to the target table, you remove the WHERE clause. Otherwise, you can specify which rows from the source table should be copied to the target table.
Oracle INSERT INTO SELECT examples
A) Insert all sales data example
Let’s create a table named sales for the demonstration.
CREATE TABLE sales (
customer_id NUMBER,
product_id NUMBER,
order_date DATE NOT NULL,
total NUMBER(9,2) DEFAULT 0 NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(customer_id,
product_id,
order_date)
);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following statement inserts a sales summary from the orders and order_items tables into the sales table:
INSERT INTO sales(customer_id, product_id, order_date, total)
SELECT customer_id,
product_id,
order_date,
SUM(quantity * unit_price) amount
FROM orders
INNER JOIN order_items USING(order_id)
WHERE status = 'Shipped'
GROUP BY customer_id,
product_id,
order_date;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following statement retrieves data from the sales table to verify the insert:
SELECT *
FROM sales
ORDER BY order_date DESC,
total DESC;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)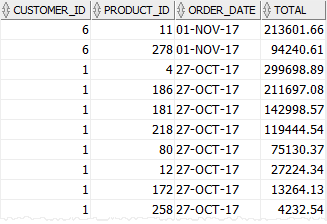
B) Insert partial sales data example
Suppose, you want to copy only sales summary data in 2017 to a new table. To do so, first, you create a new table named sales_2017 as follows:
CREATE TABLE sales_2017
AS SELECT
*
FROM
sales
WHERE
1 = 0;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The condition in the WHERE clause ensures that the data from the sales table is not copied to the sales_2017 table.
Second, use the Oracle INSERT INTO SELECT with a WHERE clause to copy 2017 sales data to the sales_2017 table:
INSERT INTO sales_2017
SELECT customer_id,
product_id,
order_date,
SUM(quantity * unit_price) amount
FROM orders
INNER JOIN order_items USING(order_id)
WHERE status = 'Shipped' AND EXTRACT(year from order_date) = 2017
GROUP BY customer_id,
product_id,
order_date;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this example, we didn’t specify the column list in the INSERT INTO clause because the result of the SELECT statement has the values that correspond to the columns of the sales_2017 table.
In addition, we added more condition to the WHERE clause of the SELECT statement to retrieve only sales data in 2017.
The following query selects all data from the sales_2017 table:
SELECT *
FROM sales_2017
ORDER BY order_date DESC,
total DESC;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)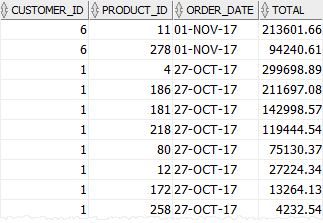
C) Insert partial data and literal value example
Suppose, you want to send emails to all customers to announce new products. To do it, you can copy customer data to a separate table and track email sending status.
First, create a new table named customer_lists as follows:
CREATE TABLE customer_lists(
list_id NUMBER GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY,
first_name varchar2(255) NOT NULL,
last_name varchar2(255) NOT NULL,
email varchar2(255) NOT NULL,
sent NUMBER(1) NOT NULL,
sent_date DATE,
PRIMARY KEY(list_id)
);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, copy data from the contacts table to the customer_lists table:
INSERT INTO
customer_lists(
first_name,
last_name,
email,
sent
) SELECT
first_name,
last_name,
email,
0
FROM
contacts;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this example, in addition to retrieving data from the contacts table, we also used literal 0 as the value for the sent column.
The following query retrieves the data from the customer_lists table:
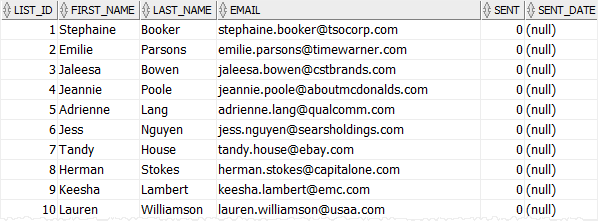
Note that this example is just for demonstration, you can add DEFAULT 0 to the definition of the sent column.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the Oracle INSERT INTO SELECT statement to insert data into a table from the result of a query.