Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the Oracle WHERE clause to specify a condition for filtering rows returned by a query.
Introduction to Oracle WHERE clause
The WHERE clause specifies a search condition for rows returned by the SELECT statement. The following illustrates the syntax of the WHERE clause:
SELECT
select_list
FROM
table_name
WHERE
search_condition
ORDER BY
sort_expression;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The WHERE clause appears after the FROM clause but before the ORDER BY clause. Following the WHERE keyword is the search_condition that defines a condition that returned rows must satisfy.
Besides the SELECT statement, you can use the WHERE clause in the DELETE or UPDATE statement to specify which rows to update or delete.
Oracle WHERE examples
See the following products table in the sample database:

A) Selecting rows by using a simple equality operator
The following example returns only products whose names are 'Kingston':
SELECT
product_name,
description,
list_price,
category_id
FROM
products
WHERE
product_name = 'Kingston';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following picture illustrates the result:
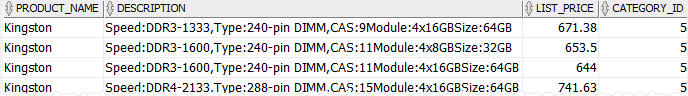
In this example, Oracle evaluates the clauses in the following order: FROM, WHERE and SELECT
- First, the
FROMclause specified the table for querying data. - Second, the
WHEREclause filtered rows based on the condition e.g.,product_name = 'Kingston'). - Third, the
SELECTclause chose the columns that should be returned.
B) Select rows using the comparison operator
Besides the equality operator, Oracle provides you with many other comparison operators illustrated in the following table:
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| = | Equality |
| !=,<> | Inequality |
| > | Greater than |
| < | Less than |
| >= | Greater than or equal to |
| <= | Less than or equal to |
| IN | Equal to any value in a list of values |
| ANY/ SOME / ALL | Compare a value to a list or subquery. It must be preceded by another operator such as =, >, <. |
| NOT IN | Not equal to any value in a list of values |
| [NOT] BETWEEN n and m | Equivalent to [Not] >= n and <= y. |
| [NOT] EXISTS | Return true if the subquery returns at least one row |
| IS [NOT] NULL | NULL test |
For example, to get products whose list prices are greater than 500, you use the following statement:
SELECT
product_name,
list_price
FROM
products
WHERE
list_price > 500;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)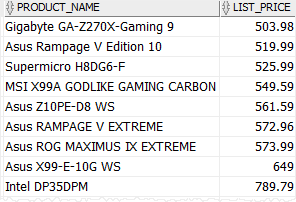
C) Select rows that meet some conditions
To combine conditions you can use the AND, OR and NOT logical operators.
For example, to get all motherboards that belong to the category id 1 and have list prices greater than 500, you use the following statement:
SELECT
product_name,
list_price
FROM
products
WHERE
list_price > 500
AND category_id = 1;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The result set includes only motherboards whose list prices are greater than 500.
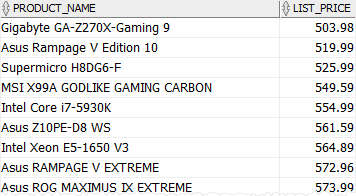
D) Selecting rows that have a value between two values
To find rows that have a value between two values, you use the BETWEEN operator in the WHERE clause.
For example, to get the products whose list prices are between 650 and 680, you use the following statement:
SELECT
product_name,
list_price
FROM
products
WHERE
list_price BETWEEN 650 AND 680
ORDER BY
list_price;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following picture illustrates the result set:
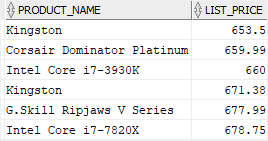
Note that the following expressions are equivalent:
list_price BETWEEN 650 AND 680
list_price >= 650 AND list_price <= 680E) Selecting rows that are in a list of values
To query rows that are in a list of values, you use the IN operator as follows:
SELECT
product_name,
category_id
FROM
products
WHERE
category_id IN(1, 4)
ORDER BY
product_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following illustrates the result:
The expression:
category_id IN (1, 4)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)is the same as:
category_id = 1 OR category_id = 4Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)F) Selecting rows which contain value as a part of a string
The following statement retrieves a product whose name starts with Asus:
SELECT
product_name,
list_price
FROM
products
WHERE
product_name LIKE 'Asus%'
ORDER BY
list_price;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this example, we used the LIKE operator to match rows based on the specified pattern.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the Oracle WHERE clause to specify a search condition for rows returned by a query.