Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the Oracle ALTER TABLE MODIFY column statement to change the definition of existing columns.
To change the definition of a column in a table, you use the ALTER TABLE MODIFY column syntax as follows:
ALTER TABLE table_name
MODIFY column_name action;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The statement is straightforward. To modify a column of a table, you need to specify the column name, table name, and action that you want to perform.
Oracle allows you to perform many actions but the following are the main ones:
- Modify the column’s visibility
- Allow or not allow null values
- Shorten or widen the size of the column
- Change the default value of a column
- Modify the expression of the virtual columns
To modify multiple columns, you use the following syntax:
ALTER TABLE table_name
MODIFY (
column_name_1 action,
column_name_2 action,
...
);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Oracle ALTER TABLE MODIFY column examples
First, create a new table named accounts for the demonstration:
CREATE TABLE accounts (
account_id NUMBER GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY,
first_name VARCHAR2(25) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR2(25) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR2(100),
phone VARCHAR2(12) ,
full_name VARCHAR2(51) GENERATED ALWAYS AS(
first_name || ' ' || last_name
),
PRIMARY KEY(account_id)
);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, insert some rows into the accounts table:
INSERT INTO accounts(first_name,last_name,phone)
VALUES('Trinity',
'Knox',
'410-555-0197');
INSERT INTO accounts(first_name,last_name,phone)
VALUES('Mellissa',
'Porter',
'410-555-0198');
INSERT INTO accounts(first_name,last_name,phone)
VALUES('Leeanna',
'Bowman',
'410-555-0199');
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Third, verify the insert operation by using the following SELECT statement:
SELECT
*
FROM
accounts;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)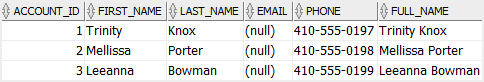
A) Modify the column’s visibility
In Oracle Database 12c, you can define table columns as invisible or visible. Invisible columns are not available for the query like:
SELECT
*
FROM
table_name;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Or statement like:
DESCRIBE table_name;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)in SQL*Plus.
However, you can query the invisible columns by specifying them explicitly in the query:
SELECT
invisible_column_1,
invisible_column_2
FROM
table_name;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)By default, table columns are visible. You can define an invisible column when you create the table or using ALTER TABLE MODIFY column statement.
For example, the following statement makes the full_name column invisible:
ALTER TABLE accounts
MODIFY full_name INVISIBLE;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)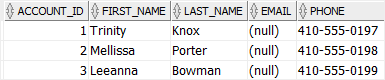
The following statement returns data from all columns of the accounts table except the full_name column:
SELECT
*
FROM
accounts;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)This is because the full_name column is invisible.
To change a column from invisible to visible, you use the statement below:
ALTER TABLE accounts
MODIFY full_name VISIBLE;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)B) Allow or not allow null example
The following statement changes the email column to accept non-null values:
ALTER TABLE accounts
MODIFY email VARCHAR2( 100 ) NOT NULL;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)However, Oracle issued the following error:
SQL Error: ORA-02296: cannot enable (OT.) - null values found
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Because when you change a column from nullable to non-nullable, you must ensure that the existing data meets the new constraint.
To fix this, we update the values for the email column first:
UPDATE
accounts
SET
email = LOWER(first_name || '.' || last_name || '@oracletutorial.com') ;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Note that the LOWER() function converts a string to lowercase.
And then change the column’s constraint:
ALTER TABLE accounts
MODIFY email VARCHAR2( 100 ) NOT NULL;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Now, it is working as expected.
C) Widen or shorten the size of a column example
Suppose, we want to add international code to the phone numbers. Before doing it, we must widen the size of the phone column by using the following statement:
ALTER TABLE accounts
MODIFY phone VARCHAR2( 15 );Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Now, we can update the phone numbers:
UPDATE
accounts
SET
phone = '+1-' || phone;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following statement verifies the update:
SELECT
*
FROM
accounts;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)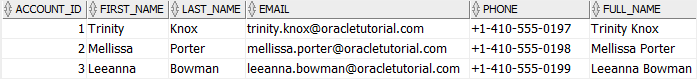
To shorten the size of a column, you make sure that all data in the column fits the new size.
For example, we try to shorten the size of the phone column down to 12 characters:
ALTER TABLE accounts
MODIFY phone VARCHAR2( 12 );Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Oracle Database issued the following error:
SQL Error: ORA-01441: cannot decrease column length because some value is too big
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To fix this, first, we should remove the international code from the phone numbers:
UPDATE
accounts
SET
phone = REPLACE(
phone,
'+1-',
''
);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The REPLACE() function replaces a substring with a new substring. In this case, it replaces the ‘+1-‘ with an empty string.
And then shorten the size of the phone column:
ALTER TABLE accounts
MODIFY phone VARCHAR2( 12 );Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)D) Modify virtual column
Suppose, we the full name in the following format:
last_name, first_nameCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To do this, we can change the expression of the virtual column full_name as follows:
ALTER TABLE accounts
MODIFY full_name VARCHAR2(52)
GENERATED ALWAYS AS (last_name || ', ' || first_name);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following statement verifies the modification:
SELECT
*
FROM
accounts;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)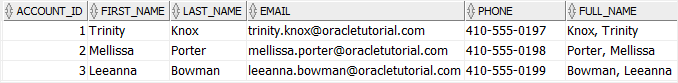
E) Modify the default value of a column
Let’s add a new column named status to the accounts table with default value 1.
ALTER TABLE accounts
ADD status NUMBER( 1, 0 ) DEFAULT 1 NOT NULL ;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)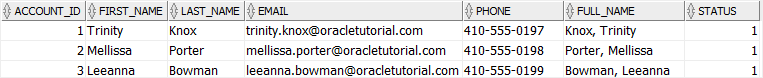
Once you execute the statement, the values in the status column are set to 1 for all existing rows in the accounts table.
To change the default value of the status column to 0, you use the following statement:
ALTER TABLE accounts
MODIFY status DEFAULT 0;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)We can add a new row to the accounts table to check whether the default value of the status column is 0 or 1:
INSERT INTO accounts ( first_name, last_name, email, phone )
VALUES ( 'Julia',
'Madden',
'[email protected]',
'410-555-0200' );
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Query data from the accounts table:
SELECT
*
FROM
accounts;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)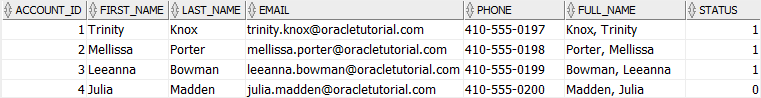
As you can see, the value in the status column for the account with id 4 is 0 as expected.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the Oracle ALTER TABLE MODIFY column statement to change the definition of existing columns in a table.