Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn about the Oracle temporary tablespaces and how to manipulate the temporary tablespaces effectively.
Introduction to Oracle Temporary Tablespaces
A temporary tablespace, as its name implies, stores the temporary data that only exists during the database session.
Oracle uses temporary tablespaces to improve the concurrency of multiple sort operations that do not fit in memory. On top of this, Oracle stores temporary tables, temporary indexes, temporary B-trees, and temporary LOBs in temporary tablespaces.
By default, Oracle creates a single temporary tablespace named TEMP for each new Oracle Database installation. This TEMP tablespace can be shared by multiple users.
Besides the TEMP default temporary tablespace, you can create additional temporary tablespaces and assign them to a user using the CREATE USER or ALTER USER statement.
Oracle default temporary tablespace
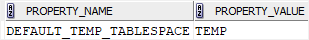
When you create a user without specifying a temporary tablespace, Oracle assigns the default temporary tablespace TEMP to user. If you want to change the default temporary tablespace, you can use the following command:
ALTER DATABASE DEFAULT TEMPORARY TABLESPACE tablespace_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To find the current default temporary tablespace, you execute the following statement:
SELECT
property_name,
property_value
FROM
database_properties
WHERE
property_name='DEFAULT_TEMP_TABLESPACE';
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the output:
Viewing space allocation in a temporary tablespace
This statement returns the space allocated and free space in a temporary tablespace:
SELECT * FROM dba_temp_free_space;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Creating a temporary tablespace
To create a new temporary tablespace, you use the CREATE TEMPORARY TABLESPACE statement:
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLESPACE tablespace_name
TEMPFILE 'path_to_file'
SIZE size;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Oracle default tablespace examples
First, create a new temporary tablespace named temp2 with the size of 100MB:
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLESPACE temp2
TEMPFILE 'temp2.dbf'
SIZE 100m;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Next, find all temporary tablespaces in the current Oracle Database:
SELECT
tablespace_name,
file_name,
bytes/1024/1024 MB,
status
FROM
dba_temp_files;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
Then, check which tablespace is the default temporary tablespace:
SELECT
property_name,
property_value
FROM
database_properties
WHERE
property_name='DEFAULT_TEMP_TABLESPACE';
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
After that, change the default temporary tablespace name to temp2:
ALTER DATABASE DEFAULT TEMPORARY TABLESPACE temp2;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Finally, drop the temp2 tablespace:
DROP TABLESPACE temp2 INCLUDING CONTENTS AND DATAFILES;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Oracle issued the following error:
SQL Error: ORA-12906: cannot drop default temporary tablespace
You cannot drop the default temporary tablespace. To delete the temp2 tablespace as the default temporary tablespace, you must first change the default tablespace back to the TEMP tablespace:
ALTER DATABASE DEFAULT TEMPORARY TABLESPACE temp;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And then drop the temp2 temporary tablespace:
DROP TABLESPACE temp2 INCLUDING CONTENTS AND DATAFILES;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this tutorial, you have learned about the Oracle temporary tablespaces and how to manipulate them effectively.