Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the Oracle CREATE USER statement to create a new user in the Oracle database.
Introduction to Oracle CREATE USER statement
The CREATE USER statement allows you to create a new database user which you can use to log in to the Oracle database.
The basic syntax of the CREATE USER statement is as follows:
CREATE USER username
IDENTIFIED BY password
[DEFAULT TABLESPACE tablespace]
[QUOTA {size | UNLIMITED} ON tablespace]
[PROFILE profile]
[PASSWORD EXPIRE]
[ACCOUNT {LOCK | UNLOCK}];Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax:
CREATE USER username
Specify the name of the user to be created.
IDENTIFIED BY password
Specify a password for the local user to use to log on to the database. Note that you can create an external or global user, which is not covered in this tutorial.
DEFAULT TABLESPACE
Specify the tablespace of the objects such as tables and views that the user will create.
If you skip this clause, the user’s objects will be stored in the database default tablespace if available, typically it is USERS tablespace; or the SYSTEM tablespace in case there is no database default tablespace.
QUOTA
Specify the maximum space in the tablespace that the user can use. You can have multiple QUOTA clauses, each for a tablespace.
Use UNLIMITED if you don’t want to restrict the size of the tablespace that the user can use.
PROFILE profile
A user profile limits the database resources or password that the user cannot exceed. You can assign a profile to a newly created user. If you skip this clause, Oracle will assign the DEFAULT profile to the user.
PASSWORD EXPIRE
Use the PASSWORD EXPIRE if you want to force the user to change the password for the first time the user logs in to the database.
ACCOUNT {LOCK | UNLOCK}
Use ACCOUNT LOCK if you want to lock the user and disable access. On the other hand, specify ACCOUNT UNLOCK to unlock user and enable access.
To execute the CREATE USER statement, you must have the CREATE USER system privilege. Once you create the new user, the privilege domain of the user will be empty.
Therefore, if you want the user to be able to login to the database, you should grant the CREATE SESSION system privilege to the user.
Oracle CREATE USER examples
Let’s practice with the CREATE USER statement.
1) Using Oracle CREATE USER statement to create a new local user example
This example uses the CREATE USER statement to create a new local user named john with the password abcd1234:
CREATE USER john IDENTIFIED BY abcd1234;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Oracle issues the following output indicating that the user john has been created successfully.
User JOHN created.
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To find a list of users with the OPEN status, you query the information from the dba_users:
SELECT
username,
default_tablespace,
profile,
authentication_type
FROM
dba_users
WHERE
account_status = 'OPEN';
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)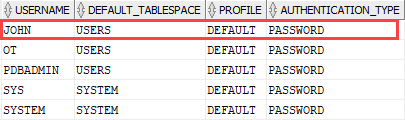
As you can see from the output, the user john has a default tablespace as USERS, profile as DEFAULT, and log in to the database using a PASSWORD.
Let’s use the john account to log in to the database.
Launch the SQL*Plus program and enter the following information:
Enter user-name: john@pdborcl
Enter password:<john_password>
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Oracle issued the following error:
ERROR: ORA-01045: user JOHN lacks CREATE SESSION privilege; logon denied
To enable the user john to log in, you need to grant the CREATE SESSION system privilege to the user john by using the following statement:
GRANT CREATE SESSION TO john;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Now, the user john should be able to log in to the database.
Enter user-name: john@pdborcl
Enter password:
Connected to:
Oracle Database 12c Enterprise Edition Release 12.2.0.1.0 - 64bit Production
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)2) Using Oracle CREATE USER statement to create a new local user with password expired example
First, use the CREATE USER statement to create a new user jane:
CREATE USER jane IDENTIFIED BY abcd1234
PASSWORD EXPIRE;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, verify if the user has been created successfully:
SELECT
username,
default_tablespace,
profile,
authentication_type
FROM
dba_users
WHERE
account_status = 'OPEN';
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)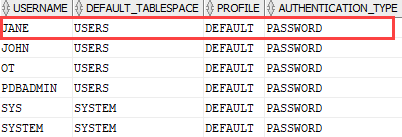
Third, grant the CREATE SESSION privilege to the user jane so that you can use this user to log in the Oracle database.
GRANT CREATE SESSION TO jane;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Finally, use the user jane to log in to the database via the SQL*plus program:
SQL> connect jane@orclpdb/abcd1234
ERROR:
ORA-28001: the password has expired
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Oracle requested to change the password for jane, you must provide the new password and confirm it before you can log in:
Changing password for jane
New password:<new_password>
Retype new password:<new_password>
Password changed
Connected.
SQL>Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the Oracle CREATE USER statement to create a new user in the Oracle database.