The Oracle REPLACE() function replaces all occurrences of a specified substring in a string with another.
Syntax #
Here’s the syntax of the Oracle REPLACE() function:
REPLACE(string_expression, string_pattern [,string_replacement])Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Arguments #
The Oracle REPLACE() function accepts three arguments:
1) string_expression
is a string (or an expression that evaluates to a string) to be searched.
2) string_pattern
is a substring to be replaced.
3) string_replacement
is the replacement string.
Return Value #
The REPLACE() function returns a string with every occurrence of the string_pattern replaced with the string_replacement.
If you omit the string_replacement, the REPLACE() function removes all occurrences of the string_pattern in the string_expression.
In case the string_pattern is null or empty, the REPLACE() function returns the string_expression.
Examples #
The following statement replaces is with 'IS' in the string ‘This is a test':
SELECT
REPLACE ('This is a test', 'is', 'IS')
FROM
dual;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
'thIS IS a test'Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)We often use the REPLACE()
Let’s create a new table named articles for the demonstration.
First, create the articles table with the following structure:
CREATE TABLE articles (
article_id NUMBER GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY,
title VARCHAR2 (255),
article_body VARCHAR2 (4000),
PRIMARY KEY (article_id)
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Next, insert sample data into the articles table:
INSERT INTO
articles (title, article_body)
VALUES
(
'Sample article',
'This is a <strong>sample</strong> article'
);
INSERT INTO
articles (title, article_body)
VALUES
(
'Another article',
'Another excellent <strong>sample</strong> article'
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Then, query data from the articles table:
SELECT
article_id,
title,
article_body
FROM
articles;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)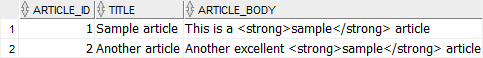
After that, suppose you want to replace all <strong> tags with <b> tags in the article_body column. Here are the queries to do so:
UPDATE articles
SET
article_body = REPLACE (article_body, '<strong>', '<b>');
UPDATE articles
SET
article_body = REPLACE (article_body, '</strong>', '</b>');Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)These queries used the REPLACE() function to replace <strong> with <b> and </strong> with </b>.
Finally, query data from the articles table to verify the replacements:
SELECT
article_id,
title,
article_body
FROM
articles;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)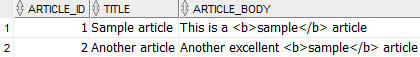
The output shows that the statement replaced the <strong> tags with the b tags.
Remarks #
Oracle provides you with the TRANSLATE() function that has similar functionality to the REPLACE() function.
However, the TRANSLATE() function provides single-character, one-to-one substitution, while the REPLACE() function allows you to substitute one string for another.
Summary #
- Use the Oracle
REPLACE()function to replace all occurrences of a substring in a string with another.