The Oracle INSTR() function searches for a substring in a string and returns the position of the substring in a string.
Syntax
The following illustrates the syntax of the Oracle INSTR() function:
INSTR(string , substring [, start_position [, occurrence]])Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Arguments
The Oracle INSTR() function accepts four arguments:
string
is the string or character expression that contains the substring to be found.
substring
is the substring to be searched
start_position
is a nonzero integer that specifies where in the string the INSTR() function begins to search. The start_position is calculated using characters as defined by the input character set.
If the start_position is positive, then INSTR() function searches and counts forward from the beginning of the string. In case the start_position is negative, the INSTR() function will search and count backward from the end of the string.
The start_position is an optional parameter. The default value of the start_position is 1. It means that, by default, the INSTR() function searches from the beginning of the string.
occurrence
is a positive integer that specifies which occurrence of the substring for which the INSTR() function should search. The occurence is optional and its default value is 1, meaning that the INSTR() funtion searches for the first occurrence of the substring by default.
Return value
The INSTR() function returns a positive integer that is the position of a substring within a string.
If the string does not contain the substring, the INSTR() function returns 0 (zero).
Examples
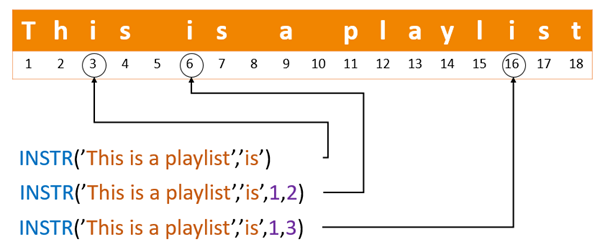
1) Search from the start of the string
The following statement returns the location of the first occurrence of the is substring in This is a playlist, starting from position 1 (the first character) in the string.
SELECT
INSTR( 'This is a playlist', 'is' ) substring_location
FROM
dual;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)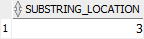
In this example, the INSTR() function searched for the first occurrence of the substring is from the beginning of the string This is a playlist.
2) Search for the 2nd and 3nd occurrence of a substring
The following statement returns the location of the 2nd and 3rd occurrences of the substring is in This is a playlist
SELECT
INSTR( 'This is a playlist', 'is', 1, 2 ) second_occurrence,
INSTR( 'This is a playlist', 'is', 1, 3 ) third_occurrence
FROM
dual;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this example, we passed the start_position as 1 and the occurrence as 2 and 3 to instruct the INSTR() function to search for the 2nd and 3rd occurrences of the substring is in the string This is a playlist.
3) Search for a substring that does not exist in a string
The following example illustrates the result when the substring are is not found in the searched string:
SELECT
INSTR( 'This is a playlist', 'are' ) substring_location
FROM
dual;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)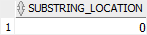
4) Search backward
The following example searches the first occurrence of the substring is backward from the end of the searched string.
SELECT
INSTR( 'This is a playlist', 'is',-1 ) substring_location
FROM
dual;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)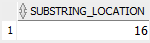
In this tutorial, you have learned how to search and return the position of a substring in a string.