The Oracle TO_DATE() function converts a date literal to a DATE value.
Syntax
The following illustrates the syntax of the Oracle TO_DATE()function:
TO_DATE (string, format, nls_language)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Arguments
The TO_DATE() function accepts three arguments:
1) string
is a string value which is converted to a DATE value. It can be a value of any data type CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, or NVARCHAR2.
2) format
is the date and time format for the string.
The format argument is optional. If you omit the format, the string must be in the standard date format which is DD-MON-YY e.g., 31-DEC-2000
Noted that if format is J, which is for Julian, then the string must be an integer.
For the detailed information on how to construct the format, check it out the Oracle date format.
3) nls_language
is an expression that specifies the language for day and month names in the string. This nls_language argument has the following form:
NLS_DATE_LANGUAGE = languageCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)This ls_language argument is optional. If you omit it, the TO_DATE() function will use the default language for your session.
Return value
The TO_DATE() function returns a DATE value which is corresponding to the input string.
Examples
A) Basic TO_DATE() function example
To convert a string to date, you use the Oracle date format elements e.g., YYYY for the 4-digit year, MM for the 2-digit month, etc.
Suppose, you have the following date literal:
'5 Jan 2017'Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To convert this string to a DATE value, first, you must construct the date format model for it. In this case, 5 is represented by DD, Jan is represented by Mon, and 2017 is represented by YYYY that results in the following format:
'DD Mon YYY'Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, you pass both arguments, date literal and format model, to the TO_DATE() function as shown below:
SELECT
TO_DATE( '5 Jan 2017', 'DD MON YYYY' )
FROM
dual;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following illustrates the output:
05-JAN-17Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)If you fail to construct the format, the TO_DATE() function will issue a respective error.
For example, if you miss one character Y in the date format model above:
SELECT
TO_DATE( '5 Jan 2017', 'DD MON YYY' )
FROM
dual;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The TO_DATE() function issued the following error:
ORA-01830: date format picture ends before converting entire input stringCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)B) Use TO_DATE() function to insert data into a table
The following statement creates a table named members:
CREATE TABLE members (
member_id NUMBER GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY,
first_name VARCHAR2 ( 50 ) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR2 ( 50 ) NOT NULL,
joined_date DATE NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY ( member_id )
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following statement inserts a new row into the members table.
INSERT INTO members(first_name, last_name, joined_date)
VALUES('Laureen','Davidson', TO_DATE('Feb 01 2017','Mon DD YYYY'));Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this example, because Feb 01 2017 is not Oracle standard date format, you have to use the TO_DATE() function to convert it to a DATE value before storing it in the table.
Here is another example of inserting a date value a DATE column using the TO_DATE() function for formatting.
INSERT INTO members(first_name, last_name, joined_date)
VALUES('Thomas','Phelps', TO_DATE('15 March 2017','DD Month YYYY'));Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)You can check whether the data was actually inserted by using the following query:
SELECT
*
FROM
members;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)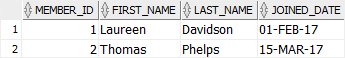
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the TO_DATE() function to convert a string into a DATE value.