Summary: In this tutorial, you will learn about the Oracle DUAL table, which is a special table used for evaluating expressions or calling functions.
Introduction to the Oracle dual table #
In Oracle, the SELECT statement must have a FROM clause. However, some queries don’t require any table, for example:
SELECT
UPPER('This is a string')
FROM
what_table;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this case, you might think about creating a table and using it in the FROM clause for just using the UPPER() function.
Fortunately, Oracle provides you with the DUAL table, which is a special table that belongs to the schema of the user SYS but it is accessible to all users.
The DUAL table has one column named DUMMY whose data type is VARCHAR2() and contains one row with a value X.
SELECT * FROM dual;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)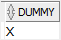
By using the DUAL table, you can execute queries that contain functions that do not involve any table, like the UPPER() function as follows:
SELECT
UPPER('This is a string')
FROM
dual;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Besides calling built-in functions, you can use expressions in the SELECT clause of a query that accesses the DUAL table:
SELECT
(10 + 5)/2
FROM
dual;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The DUAL table is the simplest one because it was designed for fast access.
Why is it called dual? #
The table name dual relates to its duality or singularity:
- Single row: The dual table has a single row, making it ideal for evaluating expressions that return a single value.
- Universally accessible: The dual table serves as a single, universally available table.
When would you use the dual table #
In practice, you’ll use the dual table in the following scenarios:
Evaluating expressions #
When you want to evaluate an expression without referencing a specific table, you use the dual table. For example:
SELECT 10 / 3 AS result FROM dual;Code language: PHP (php)Calling built-in Oracle functions #
Oracle has many built-in functions. If you call a function without referencing a specific table, you can use the dual table:
SELECT concat('Oracle ', 'Tutorial') AS result
FROM dual;Code language: PHP (php)Output:
RESULT
__________________
Oracle Tutorial Performance #
In Oracle 10g release 1 and above, Oracle treats the use of DUAL table the same as calling a function that evaluates the expression used in the select list.
This optimization provides even better performance than directly accessing the physical DUAL table.
Summary #
- The
dualtable is a dummy table that has a column and one row. - Use the
dualtable when you evaluate an expression or call functions without referencing a specific table.