Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the Oracle ANY operator to compare a value with a list or subquery.
Introduction to the Oracle ANY operator #
The Oracle ANY operator allows you to compare a value to a list of values or result set returned by a subquery.
Here’s the the syntax of the ANY operator with a list of literal values:
operator ANY ( v1, v2, v3)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And with a subquery:
operator ANY ( subquery) In this syntax:
- The
ANYoperator must be preceded by a comparison operator such as =, !=, >, >=,<, <=. - The list or subquery must be surrounded by the parentheses.
If at least one comparison returns true, the ANY operator returns true or false otherwise.
If the subquery returns an empty result set, the ANY operator always returns true.
When you use the ANY operator to compare a value to a list, Oracle expands the initial condition to all elements of the list and uses the OR operator to combine them:
SELECT
select_list
FROM
table_name
WHERE
c > ANY (v1, v2, v3);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Oracle performs a transformation of the above query to the following:
SELECT
select_list
FROM
table_name
WHERE
c > v1
OR c > v2
OR c > v3;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)If you use the ANY operator to compare a value with values from a result set returned by a subquery, Oracle uses the EXISTS operator to transform the query to an equivalent one without using the ANY operator.
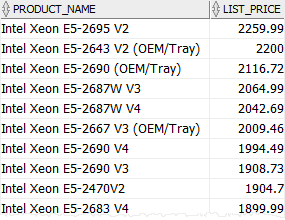
For example, the following statement returns all products whose list price is greater than any list price of products in the category 1:
SELECT
product_name,
list_price
FROM
products
WHERE
list_price > ANY (
SELECT
list_price
FROM
products
WHERE
category_id = 1
)
ORDER BY
product_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Since the query uses a subquery with the ANY operator, Oracle performs a single transformation:
SELECT
product_name,
list_price
FROM
products p1
WHERE
EXISTS (
SELECT
list_price
FROM
products p2
WHERE
category_id = 1
AND p1.list_price > p2.list_price
)
ORDER BY
product_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Note that if the subquery returns no rows, the following condition evaluates to false:
operator ANY (subquery)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Hence, the whole query returns no rows:
SELECT
select_list
FROM
table_name
WHERE
col operator ANY (subquery);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In Oracle, the SOME and ANY operators behave exactly the same therefore they are completely interchangeable.
Oracle ANY operator examples #
If the subquery returns rows or a list has value, the following statements apply to the ANY operator:
col = ANY ( list ) #
The expression evaluates to true if the col matches one or more values in the list, for example:
SELECT
product_name,
list_price
FROM
products
WHERE
list_price = ANY (2200, 2259.99, 2269.99)
AND category_id = 1;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)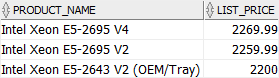
col != ANY(list) #
The expression evaluates to true if the col does not match one or more values in the list.
SELECT
product_name,
list_price
FROM
products
WHERE
list_price != ANY (2200, 2259.99, 2269.99)
AND category_id = 1
ORDER BY
list_price DESC;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)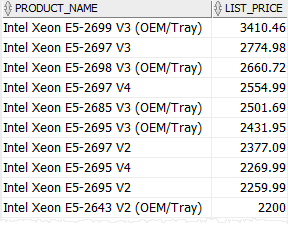
col > ANY (list) #
The expression evaluates to true if the col is greater than the smallest value in the list.
SELECT
product_name,
list_price
FROM
products
WHERE
list_price > ANY (2200, 2259.99, 2269.99)
AND category_id = 1
ORDER BY
list_price DESC;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)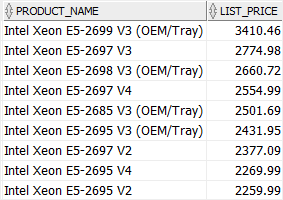
col >= ANY (list) #
The expression evaluates to true if the col is greater than or equal to the smallest value in the list.
SELECT
product_name,
list_price
FROM
products
WHERE
list_price >= ANY (2200, 2259.99, 2269.99)
AND category_id = 1
ORDER BY
list_price DESC;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)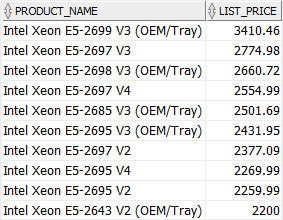
col < ANY (list) #
The expression evaluates to true if the col is smaller than the highest value in the list.
SELECT
product_name,
list_price
FROM
products
WHERE
list_price < ANY (2200, 2259.99, 2269.99)
AND category_id = 1
ORDER BY
list_price DESC;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql) #
#
col <= ANY (list) #
The expression evaluates to true if the col is smaller than or equal to the highest value in the list.
SELECT
product_name,
list_price
FROM
products
WHERE
list_price <= ANY (2200, 2259.99, 2269.99)
AND category_id = 1
ORDER BY
list_price DESC;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)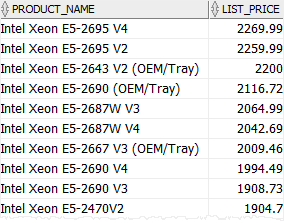
Summary #
- Use the Oracle
ANYoperator to compare a value with a list or subquery.