Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to rename a table in the database using the Oracle RENAME table statement.
Introduction to the Oracle RENAME table statement #
To rename a table, you use the following Oracle RENAME table statement as follows:
RENAME table_name TO new_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In the RENAME table statement:
- First, specify the name of the existing table which you want to rename.
- Second, provide the new table name. The new name must not be the same as another table in the same schema.
Note that you cannot roll back a RENAME statement once you executed it.
Alternatively, you can rename a table using the ALTER TABLE RENAME TO statement:
ALTER TABLE table_name
RENAME TO new_name;Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)Renaming a table using RENAME TO statement #
First, create a table named promotions for the demonstration:
CREATE TABLE promotions(
promotion_id NUMBER GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY,
promotion_name varchar2(255),
start_date DATE NOT NULL,
end_date DATE NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(promotion_id),
CHECK (end_date > start_date)
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, rename the promotions table to campaigns:
RENAME promotions TO campaigns;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Renaming a table using the ALTER TABLE statement #
The following statement renames the campaigns table back to the promotions table:
ALTER TABLE campaigns
RENAME TO promotions;Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)Invalidating objects #
When you rename a table, Oracle automatically transfers indexes, constraints, and grants from the old table to the new one. Additionally, it invalidates all objects that depend on the renamed table such as views, procedures, functions, and synonyms.
Let’s take an example.
First, define a PL/SQL function returns the number of promotions by querying data from the promotions table:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION count_promotions
RETURN NUMBER
IS
v_count NUMBER;
BEGIN
SELECT
COUNT( * )
INTO
v_count
FROM
promotions;
RETURN v_count;
END;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, rename the promotions table to campaigns:
ALTER TABLE promotions
RENAME TO campaigns;Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)Third, show the constraints of the new campaigns table transferred from the promotions table:
SELECT
constraint_name,
search_condition
FROM
all_constraints
WHERE
table_name = 'CAMPAIGNS'
AND constraint_type = 'C';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)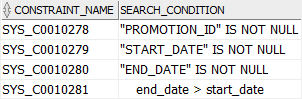
Since the COUNT_PROMOTIONS function references to promotions table, when you rename the promotions table, the COUNT_PROMOTIONS function became invalid.
Finally, find the invalid objects in the current schema by querying data from the all_objects view as follows:
SELECT
owner,
object_type,
object_name
FROM
all_objects
WHERE
status = 'INVALID'
ORDER BY
object_type,
object_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)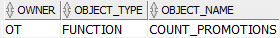
The output indicates that the COUNT_PROMOTIONS function is an invalid object.
Summary #
- Use the Oracle
RENAMEtable statement to rename an existing table in the database.