The Oracle EXTRACT() function extracts a specific component (year, month, day, hour, minute, second, etc.,) from a datetime or an interval value.
Syntax #
The following illustrates the syntax of the Oracle EXTRACT() function:
EXTRACT(field FROM source)
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)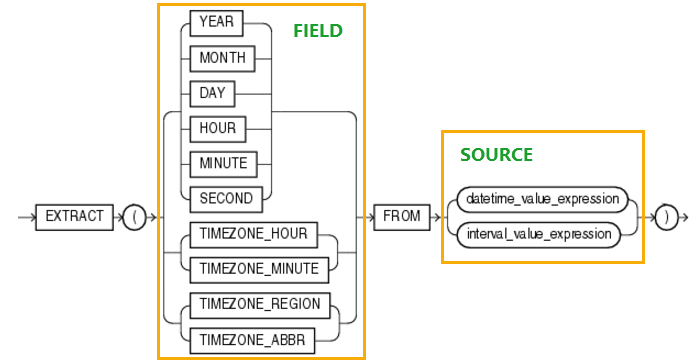
Arguments #
The Oracle EXTRACT() function accepts two arguments:
1) field
The field argument specifies the component to be extracted.
2) source
The source argument is a DATE, an INTERVAL, or a TIMESTAMP value from which a field is extracted.
The following table illustrates which fields you can extract from which value type.
| Value Type | Available Fields |
|---|---|
| DATE | YEAR, MONTH, DAY |
| INTERVAL YEAR TO MONTH | YEAR, MONTH |
| INTERVAL DAY TO SECOND | DAY, HOUR, MINUTE, SECOND |
| TIMESTAMP | YEAR, MONTH, DAY, HOUR, MINUTE, SECOND |
Note that the EXTRACT() function will return UNKNOWN if the combination of field and source result in ambiguity.
Return value #
The EXTRACT() function returns the value of the field of the source.
Examples #
A) Extracting fields from DATE values #
You can extract YEAR, MONTH, and DAY from a DATE value by using the EXTRACT() function.
The following example extracts the value of the YEAR field from a DATE value.
SELECT
EXTRACT( YEAR FROM TO_DATE( '31-Dec-1999 15:30:20 ', 'DD-Mon-YYYY HH24:MI:SS' ) ) YEAR
FROM
DUAL;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this example, we used the TO_DATE() function to convert a date literal to a DATE value.
Here is the result:
1999Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Similarly, you can extract the values of other fields as shown below:
Extracting month from a date:
SELECT
EXTRACT( MONTH FROM TO_DATE( '31-Dec-1999 15:30:20 ', 'DD-Mon-YYYY HH24:MI:SS' ) ) MONTH
FROM
DUAL;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Result
12
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Extracting day from a date:
SELECT
EXTRACT( DAY FROM TO_DATE( '31-Dec-1999 15:30:20 ', 'DD-Mon-YYYY HH24:MI:SS' ) ) DAY
FROM
DUAL;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Result
31
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To extract values of HOUR, MINUTE, and SECOND fields, you use TO_CHAR() function.
For example, to extract the hour, minute, and second of a current system date, you use the following statement:
SELECT
TO_CHAR( SYSDATE, 'HH24' ) hour,
TO_CHAR( SYSDATE, 'MI' ) minute,
TO_CHAR( SYSDATE, 'SS' ) second
FROM
DUAL;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)B) Extracting fields from INTERVAL YEAR TO MONTH values #
For the INTERVAL YEAR TO MONTH, you can extract only the YEAR and MONTH fields.
Suppose you have the following interval:
INTERVAL '5-2' YEAR TO MONTHCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)It is 5 years and 2 months.
To extract the value of the year field, you use the following statement:
SELECT
EXTRACT( YEAR FROM INTERVAL '5-2' YEAR TO MONTH )
FROM
DUAL;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The result is
5Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following example extracts the value of the month field from the interval:
SELECT
EXTRACT( MONTH FROM INTERVAL '5-2' YEAR TO MONTH )
FROM
DUAL;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the result:
2
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)C) Extracting fields from INTERVAL DAY TO SECOND values #
For an INTERVAL DAY TO SECOND, you can extract DAY, HOUR, MINUTE, and SECOND, as shown in the following example:
Extract day from an interval
SELECT
EXTRACT( DAY FROM INTERVAL '5 04:30:20.11' DAY TO SECOND )
FROM
dual;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Result:
5
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Extract hours from an interval
SELECT
EXTRACT( HOUR FROM INTERVAL '5 04:30:20.11' DAY TO SECOND )
FROM
dual;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Result:
4
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Extract minutes from an interval
SELECT
EXTRACT( MINUTE FROM INTERVAL '5 04:30:20.11' DAY TO SECOND )
FROM
dual;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Result:
30
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Extract seconds from an interval
SELECT
EXTRACT( SECOND FROM INTERVAL '5 04:30:20.11' DAY TO SECOND )
FROM
dual;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Result:
20.11
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)D) Extracting fields from TIMESTAMP values #
You can extract YEAR, MONTH, DAY, HOUR, MINUTE, and SECOND from a TIMESTAMP value as shown in the following examples:
Extracting years from a timestamp:
SELECT
EXTRACT( YEAR FROM TIMESTAMP '1999-12-31 23:59:59.10' )
FROM
dual;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Result
1999
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Extracting months from a timestamp:
SELECT
EXTRACT( MONTH FROM TIMESTAMP '1999-12-31 23:59:59.10' )
FROM
dual;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Result
12Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Extracting day from a timestamp:
SELECT
EXTRACT( DAY FROM TIMESTAMP '1999-12-31 23:59:59.10' )
FROM
dual; Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Result
31
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Extracting hours from a timestamp:
SELECT
EXTRACT( HOUR FROM TIMESTAMP '1999-12-31 23:59:59.10' )
FROM
dual;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Result
23Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Extracting minutes from a timestamp:
SELECT
EXTRACT( MINUTE FROM TIMESTAMP '1999-12-31 23:59:59.10' )
FROM
dual;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Result
59
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Extracting seconds from a timestamp:
SELECT
EXTRACT( SECOND FROM TIMESTAMP '1999-12-31 23:59:59.10' )
FROM
dual;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Result
59.10
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)E) Extracting date components from table data #
See the following orders table from the sample database:

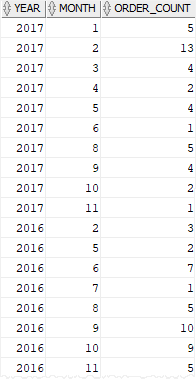
The following statement uses the EXTRACT() function to extract the year and month from the order date and return the number of orders per month:
SELECT
EXTRACT(year FROM order_date) year,
EXTRACT(month FROM order_date) month,
COUNT(order_id) order_count
FROM orders
GROUP BY
EXTRACT(YEAR FROM order_date),
EXTRACT(MONTH FROM order_date)
ORDER BY year DESC, month;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Result
F) Extracting date from user input #
The following statement attempts to extract the year, month, and day from a date that the user inputs:
SELECT
EXTRACT(YEAR FROM :input_date) year,
EXTRACT(MONTH FROM :input_date) month,
EXTRACT(DAY FROM :input_date) day
FROM dual;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)However, Oracle issued an error:
ORA-30076: invalid extract field for extract source
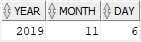
To fix this error, you need to convert the input date to a date value using the TO_DATE function. Suppose that the format of the input date is YYYYMMDD:
SELECT
EXTRACT(YEAR FROM TO_DATE(:input_date,'yyyymmdd')) year,
EXTRACT(MONTH FROM TO_DATE(:input_date,'yyyymmdd')) month,
EXTRACT(DAY FROM TO_DATE(:input_date,'yyyymmdd')) day
FROM dual;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And when you enter the input date as 20191126, the output is as follows:
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the Oracle EXTRACT() function to extract the value of a specified field of a date-time value.