Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn about the inline view in Oracle and how to use it to simplify complex queries or condense several separate queries into one.
Introduction to the inline view in Oracle #
An inline view is not a real view but a subquery in the FROM clause of a SELECT statement. Consider the following SELECT statement:
SELECT
column_list
FROM
table_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In the FROM clause, you can specify a table from which you want to query data. Besides a table, you can use a subquery as shown in the following example:
SELECT
column_list
FROM
(
SELECT
*
FROM
table_name
) t;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The subquery specified in the FROM clause of a query is called an inline view. Because an inline view can replace a table in a query, it is also called a derived table. Sometimes, you may hear the term subselect, which is the same meaning as the inline view.
You often use the inline view in Oracle to simplify complex queries by eliminating join operations or condensing separate queries into a single query.
Oracle inline view example #
Let’s use the products table in the sample database for the demonstration.

Basic Oracle inline view example #
The following query retrieves the top 10 most expensive products from the products table:
SELECT
*
FROM
(
SELECT
product_id,
product_name,
list_price
FROM
products
ORDER BY
list_price DESC
)
WHERE
ROWNUM <= 10;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)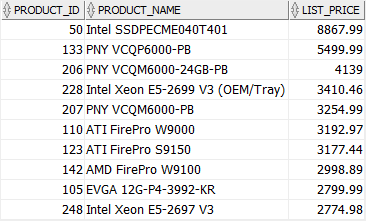
In this example, first, the inline view returns all products sorted by list prices in descending order. And then the outer query retrieves the first 10 rows from the inline view.
Inline view joins with a table example #
The following example joins an inline view with a table in the FROM clause. It returns the product categories and the highest list price of products in each category:
SELECT
category_name,
max_list_price
FROM
product_categories a,
(
SELECT
category_id,
MAX(list_price) max_list_price
FROM
products
GROUP BY
category_id
) b
WHERE
a.category_id = b.category_id
ORDER BY
category_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)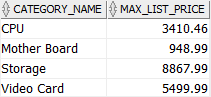
In this example, the inline view returns the category id list and the highest list price of the product in each category. The outer query joins the inline view with the product_categories table to get the category name.
LATERAL inline view example #
Consider the following statement:
SELECT
category_name,
product_name
FROM
products p,
(
SELECT
*
FROM
product_categories c
WHERE
c.category_id = p.category_id
)
ORDER BY
product_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Oracle issued an error:
ORA-00904: "P"."CATEGORY_ID": invalid identifierCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)This is because the inline view cannot reference the tables from the outside of its definition.
Fortunately, since Oracle 12c, by using the LATERAL keyword, an inline view can reference the table on the left of the inline view definition in the FROM clause as shown in the following example:
SELECT
product_name,
category_name
FROM
products p,
LATERAL (
SELECT
*
FROM
product_categories c
WHERE
c.category_id = p.category_id
)
ORDER BY
product_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)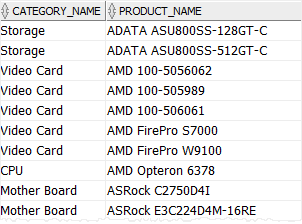
Note that the LATERAL inline views are subject to some restrictions listed in the documentation.
Oracle inline view: data manipulation examples #
You can issue data manipulation statements such as INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE against the updatable inline view.
For example, the following statement increases the list prices of CPU products by 15%:
UPDATE (
SELECT
list_price
FROM
products
INNER JOIN product_categories USING (category_id)
WHERE
category_name = 'CPU'
)
SET
list_price = list_price * 1.15;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following example deletes all video cards with a list price of less than 1,000:
DELETE (
SELECT
list_price
FROM
products
INNER JOIN product_categories USING (category_id)
WHERE
category_name = 'Video Card'
)
WHERE
list_price < 1000;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this tutorial, you have learned about the inline view in Oracle to simplify complex queries and condense several separate queries into one query.