Summary: In this tutorial, you’ll learn about Oracle views, which are essential components in Oracle Database.
Introduction to the Oracle View #
The result of a query is a derived table as shown in the following example:
SELECT
name,
credit_limit
FROM
customers;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
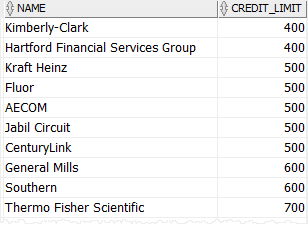
The derived table consists of the name credit limit (credit_limit) columns with many rows. It contains only partial data from the customers table.
If you assign this query a name, then you have a view. This is why a view is often referred to as a named query.
By definition, a view is a “virtual” table whose data is the result of a stored query, which is derived each time you run a query against view.
A view is a virtual table because you can use it like a table in your SQL statements. Every view has columns with data types, so you can execute a query against views or manage their contents (with some restrictions) using the INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, and MERGE statements.
Unlike a table, a view does not store any data. To be precise, a view only behaves like a table. It is simply a named query stored in the database. When you query data from a view, Oracle uses this stored query to retrieve the data from the underlying tables.
Suppose we assign the query above a name called customer_credits and query data from this view:
SELECT
*
FROM
customer_credits;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Behind the scenes, Oracle finds the stored query associated with the name customer_credits and executes the following query:
SELECT
*
FROM
(
SELECT
name,
credit_limit
FROM
customers
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this example, the customers table is called a base table. Additionally, a query that defines the view is referred to as a defining query.
The result set returned from the customer_credits view depends on the data of the underlying table, which is the customers table in this case. The customer_credits view is also dependent on the structure of the customers table.
If you rename or drop one of the columns referenced by the query, such as name or credit_limit, the view customer_credits will not work anymore.
When to use the Oracle view #
You can use views for various purposes in many cases. The most common use cases of views are:
- Simplifying data retrieval.
- Maintaining logical data independence.
- Implementing data security.
Simplifying data retrieval #
Views help simplify data retrieval significantly. First, you build a complex query, test it carefully, and encapsulate the query in a view. Then, you can access the data of the underlying tables through the view, eliminating the need to rewrite the entire query repeatedly.
For example, the following query returns the sales amount by the customer by year:
SELECT
name AS customer,
SUM(quantity * unit_price) sales_amount,
EXTRACT(
YEAR
FROM
order_date
) sales_year
FROM
orders
INNER JOIN order_items USING (order_id)
INNER JOIN customers USING (customer_id)
WHERE
status = 'Shipped'
GROUP BY
name,
EXTRACT(
YEAR
FROM
order_date
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
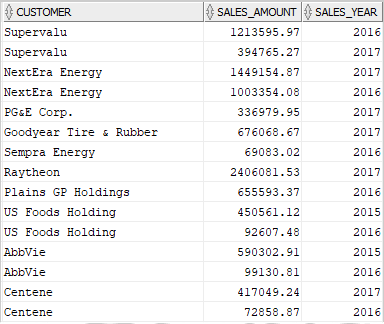
This query is quite complex. Typing it over and over again is time-consuming and can lead to mistakes. To simplify it, you can create a view based on this query:
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW customer_sales AS
SELECT
name AS customer,
SUM(quantity * unit_price) sales_amount,
EXTRACT(YEAR FROM order_date) sales_year
FROM
orders
INNER JOIN order_items USING (order_id)
INNER JOIN customers USING (customer_id)
WHERE
status = 'Shipped'
GROUP BY
name,
EXTRACT(
YEAR
FROM
order_date
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)By adding the following clause before the query, you’ll create the customer_sales view:
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW customer_sales ASCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Note that you will learn how to create views in the next tutorial.
Now, you can easily retrieve the sales by the customer in 2017 with a more straightforward query:
SELECT
customer,
sales_amount
FROM
customer_sales
WHERE
sales_year = 2017
ORDER BY
sales_amount DESC;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
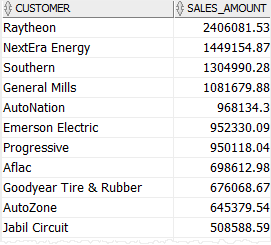
Maintaining logical data independence #
You can expose the data from underlying tables to the external applications via views. Whenever the structures of the base tables change, you need to update the view. The interface between the database and the external applications remains intact. The beauty is that you don’t have to change a single line of code to keep the external applications up and running.
For example, some reporting systems may require only customer sales data to compose strategic reports. Hence, you can give the application owners the customer_sales view.
Implementing data security #
Views allow you to implement an additional security layer. They help you hide specific columns and rows from the underlying tables, exposing only the necessary data to the relevant users.
Oracle provides you with GRANT and REVOKE commands on views, allowing you to specify which actions a user can perform against the view. Note that in this case, you don’t grant any privileges on the underlying tables because you may not want the user to bypass the views and access the base tables directly.
Summary #
- Views are named queries stored in the Oracle database.