Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the PL/SQL SELECT INTO statement to fetch data of a single row from a table into variables.
PL/SQL SELECT INTO statement is the simplest and fastest way to fetch a single row from a table into variables. The following illustrates the syntax of the PL/SQL SELECT INTO statement:
SELECT
select_list
INTO
variable_list
FROM
table_name
WHERE
condition; Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)In this syntax, the number of columns in the variable_list must be the same as the number of variables (or the number of components of a record) in the select_list. In addition, their corresponding data type must be compatible.
Besides the WHERE clause, you can use other clauses in the SELECT statement such as INNER JOIN, GROUP BY, HAVING, and UNION.
If the SELECT statement returns more than one row, Oracle will raise the TOO_MANY_ROWS exception. If the SELECT statement does not return any row, Oracle will raise the NO_DATA_FOUND exception.
PL/SQL SELECT INTO examples
Let’s use the customers and contacts tables in the sample database for demonstration.
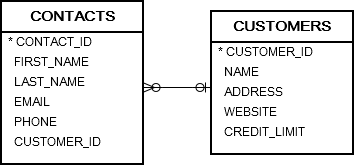
1) Selecting one column example
The following example uses a SELECT INTO statement to get the name of a customer based on the customer id, which is the primary key of the customers table.
DECLARE
l_customer_name customers.name%TYPE;
BEGIN
-- get name of the customer 100 and assign it to l_customer_name
SELECT name INTO l_customer_name
FROM customers
WHERE customer_id = 100;
-- show the customer name
dbms_output.put_line( l_customer_name );
END;Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)In this example:
- First, declare a variable
l_customer_namewhose data type anchors to the name columns of thecustomerstable. This variable will hold the customer’s name. - Second, use the
SELECT INTOstatement to select a value from the name column and assign it to thel_customer_namevariable. - Third, show the customer’s name using the
dbms_output.put_lineprocedure.
Because the customers table has only one row with customer ID 100, the code block displays the customer name.
VerizonCode language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)If there were no such row, the code block would fail with an unhandled NO_DATA_FOUND exception.
2) Selecting a complete row example
The following example fetches the entire row from the customers table for a specific customer ID:
DECLARE
r_customer customers%ROWTYPE;
BEGIN
-- get the information of the customer 100
SELECT * INTO r_customer
FROM customers
WHERE customer_id = 100;
-- show the customer info
dbms_output.put_line( r_customer.name || ', website: ' || r_customer.website );
END;Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)Here is the output:
Verizon, website: http://www.verizon.comCode language: JavaScript (javascript)In this example:
- First, declare a record based on the row of the
customerstable. This record will hold the entire row of thecustomerstable. - Second, select the customer whose id is 100 into the
r_customerrecord. - Third, show the customer’s name and website.
3) Selecting data into multiple variables example
The following example fetches the names of customers and contacts from the customers and contacts tables for a specific customer id.
DECLARE
l_customer_name customers.name%TYPE;
l_contact_first_name contacts.first_name%TYPE;
l_contact_last_name contacts.last_name%TYPE;
BEGIN
-- get customer and contact names
SELECT
name,
first_name,
last_name
INTO
l_customer_name,
l_contact_first_name,
l_contact_last_name
FROM
customers
INNER JOIN contacts USING( customer_id )
WHERE
customer_id = 100;
-- show the information
dbms_output.put_line(
l_customer_name || ', Contact Person: ' ||
l_contact_first_name || ' ' || l_contact_last_name );
END;Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)Oracle issued the following output:
Verizon, Contact Person: Elisha LloydCode language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)In this example:
- First, declare three variables
l_customer_name,l_contact_first_name,l_contact_last_nameto hold the customer and contact’s name. - Second, use the
SELECT INTOstatement to fetch the customer and contact names of the customer id 100 from thecustomersandcontactstables into the corresponding variables l_customer_name,l_contact_first_name,l_contact_last_name.- Third, display the customer and contact names.
PL/SQL SELECT INTO common errors
If the number of columns and expressions in the SELECT clause is greater than the number of variables in the INTO clause, Oracle issues this error:
ORA-00947: not enough values The INTO list contains fewer variables than the SELECT list.Code language: PHP (php)Oracle issues the following error if the number of columns and expressions in the SELECT clause is less than the number of variables in the INTO clause:
ORA-00913: too many values The INTO list contains more variables than the SELECT list.Code language: PHP (php)If the number of variables and elements in the select list are the same, but their corresponding datatypes are not compatible, Oracle cannot implicitly convert from one type to the other. It will issue the following error:
ORA-06502: PL/SQL: numeric or value errorCode language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)Now, you should know how to use the PL/SQL SELECT INTO statement to fetch a single row from a table into variables.