Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to develop a PL/SQL function and how to call it in various places such as an assignment statement, a Boolean expression, and an SQL statement.
Creating a PL/SQL function
Similar to a procedure, a PL/SQL function is a reusable program unit stored as a schema object in the Oracle Database. The following illustrates the syntax for creating a function:
CREATE [OR REPLACE] FUNCTION function_name (parameter_list)
RETURN return_type
IS
[declarative section]
BEGIN
[executable section]
[EXCEPTION]
[exception-handling section]
END;Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)A function consists of a header and body.
The function header has the function name and a RETURN clause that specifies the datatype of the returned value. Each parameter of the function can be either in the IN, OUT, or INOUT mode. For more information on the parameter mode, check it out the PL/SQL procedure tutorial
The function body is the same as the procedure body which has three sections: declarative section, executable section, and exception-handling section.
- The declarative section is between the
ISandBEGINkeywords. It is where you declare variables, constants, cursors, and user-defined types. - The executable section is between the
BEGINandENDkeywords. It is where you place the executable statements. Unlike a procedure, you must have at least oneRETURNstatement in the executable statement. - The exception-handling section is where you put the exception handler code.
In these three sections, only the executable section is required, the others are optional.
PL/SQL function example
The following example creates a function that calculates total sales by year.
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION get_total_sales(
in_year PLS_INTEGER
)
RETURN NUMBER
IS
l_total_sales NUMBER := 0;
BEGIN
-- get total sales
SELECT SUM(unit_price * quantity)
INTO l_total_sales
FROM order_items
INNER JOIN orders USING (order_id)
WHERE status = 'Shipped'
GROUP BY EXTRACT(YEAR FROM order_date)
HAVING EXTRACT(YEAR FROM order_date) = in_year;
-- return the total sales
RETURN l_total_sales;
END;Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)To compile the function in Oracle SQL Developer, you click the Run Statement button as shown in the picture below:
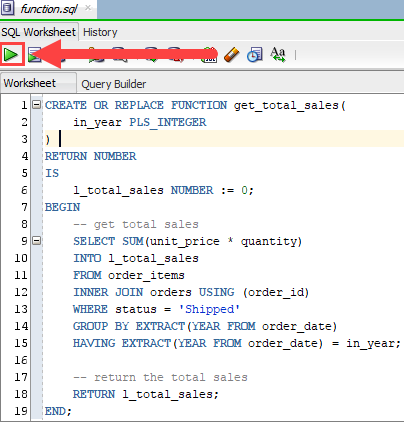
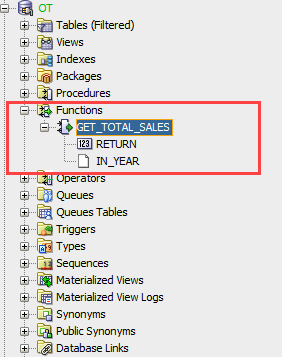
Once the function is compiled successfully, you can find it under the Functions node:
Calling a PL/SQL function
You use a function anywhere that you use an expression of the same type. You can call a function in various places such as:
1) in an assignment statement:
DECLARE
l_sales_2017 NUMBER := 0;
BEGIN
l_sales_2017 := get_total_sales (2017);
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Sales 2017: ' || l_sales_2017);
END;
Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)2) in a Boolean expression
BEGIN
IF get_total_sales (2017) > 10000000 THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Sales 2017 is above target');
END IF;
END;
Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)3) in an SQL statement
SELECT
get_total_sales(2017)
FROM
dual;
Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)Editing a function
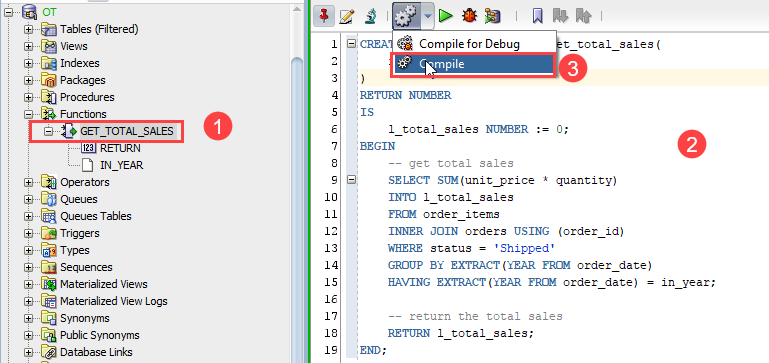
To edit and recompile an existing function, you follow these steps:
- First, click the function name that you want to edit
- Second, edit the code.
- Third, click the Compile menu option to recompile the code.
Removing a function
The DROP FUNCTION deletes a function from the Oracle Database. The syntax for removing a function is straightforward:
DROP FUNCTION function_name;
Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)Followed by the DROP FUNCTION keywords is the function name that you want to drop.
For example, the following statement drops the GET_TOTAL_SALES function:
DROP FUNCTION get_total_sales;
Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)Oracle issued a message indicating that the function GET_TOTAL_SALES has been dropped:
Function GET_TOTAL_SALES dropped.
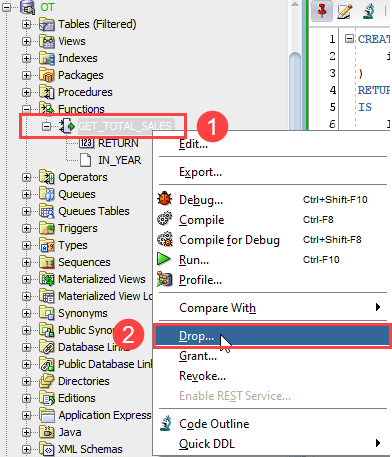
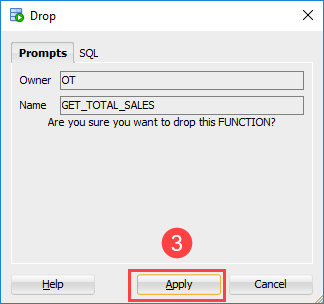
Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)If you want to drop a function using the SQL Developer, you can use these steps:
- First, right click on the name of function that you want to delete.
- Second, choose the Drop… menu option.
- Third, click the Apply button to confirm the deletion.
Now, you should know how to develop a PL/SQL function and call it in your program.