Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to enable a trigger or all triggers of a table in the database.
Enable a trigger
To enable a previously disabled trigger, you use the ALTER TRIGGER ENABLE statement:
ALTER TRIGGER trigger_name ENABLE;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax, you place the name of the trigger that you want to disable after the ALTER TRIGGER keywords.
For example, the following statement enables the customers_audit_trg trigger:
ALTER TRIGGER customers_audit_trg ENABLE;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Once the trigger is enabled, you can see its color changes from gray to orange:
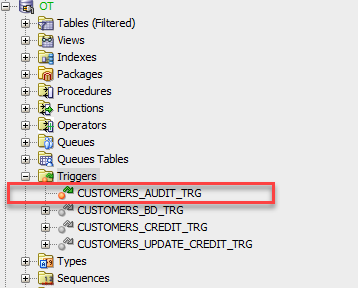
Enable all triggers of a table
To enable all triggers of a table, you can use the ALTER TABLE ... ENABLE ALL TRIGGERS statement:
ALTER TABLE table_name
ENABLE ALL TRIGGERS;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax, you put the name of the table in which you want to enable all triggers.
For example, this statement enables all triggers of the customers table:
ALTER TABLE customers
ENABLE ALL TRIGGERS;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this tutorial, you have learned how to enable a trigger or all triggers of a table in the Oracle Database.