Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the Oracle STARTUP command to start an Oracle Database instance.
To start up a database instance, you use the STARTUP command:
STARTUP
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)When the Oracle Database starts an instance, it goes through the following stages: NOMOUNT, MOUNT, and OPEN.
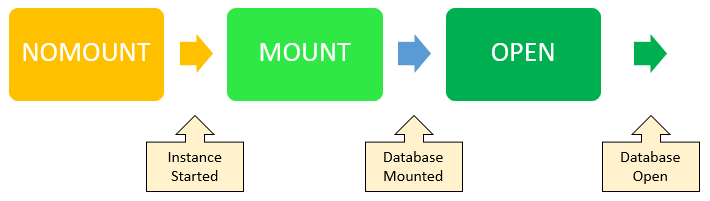
The STARTUP command allows you to control the stage of the database instance.
1) NOMOUNT stage
In the NOMOUNT stage, Oracle carries the following steps:
- First, search for a server parameter file in the default location. You can override the default behavior by using the
SPFILEorPFILEparameters in theSTARTUPcommand. - Next, read the parameter file to get the values of the initialization parameters.
- Then, allocate the system global area (SGA) based on the initialization parameter settings.
- After that, start the Oracle background processes such as
SMON,PMON, andLGWR. - Finally, open the alert log and trace files and record all explicit parameters to the alert log in the valid parameter syntax.
At the NOMOUNT stage, Oracle does not associate the database with the instance.
2) MOUNT stage
In the MOUNT stage, Oracle associates a database with an instance. In other words, the instance mounts the database.
The instance carries the following steps to mount a database:
- First, get the name of the database control files specified in the
CONTROL_FILEinitialization parameter. - Second, open the control files.
- Third, find the name of the data files and the online redo log files.
When a database is mounted, the database is only available to database administrators, not all users.
3) OPEN stage
In the OPEN stage, Oracle performs the following actions:
- First, open the online data files in tablespaces other than the undo tablespaces.
- Then, select an undo tablespace. The instance uses the default undo tablespace if an undo tablespace is specified in the
UNDO_TABLESPACEinitialization parameter. Otherwise, it will select the first available undo tablespace. - Finally, open the online redo log files.
When Oracle opens a mounted database, the database is available for normal operations.
The following picture illustrates the Oracle database startup process:
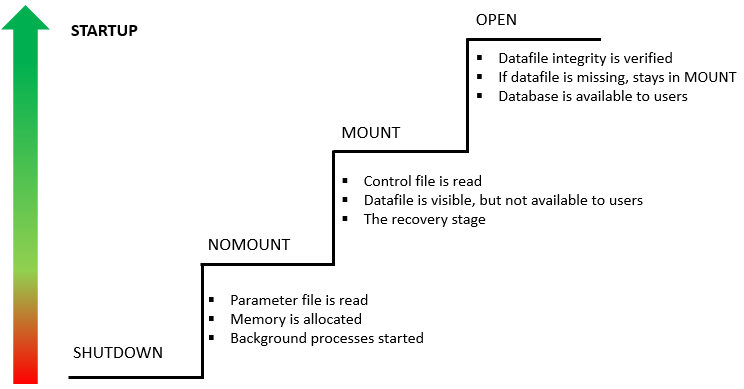
Oracle STARTUP command
The basic syntax of the STARTUP command is as follows:
STARTUP;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)It is equivalent to starting the database instance in the OPEN stage:
STARTUP OPEN;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)If you want to start the database instance in a specific stage, you can use the following syntax:
STARTUP stage;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)For example, to start up a database instance in the NOMOUNT stage, you use the following command:
STARTUP NOMOUNT;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To bring the database to the next stage, you use the ALTER DATABASE statement. For example, this statement brings the database from the NOMOUNT to the MOUNT stage:
ALTER DATABASE MOUNT;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Oracle STARTUP command example
First, launch the SQL*Plus program and log in to the Oracle Database as the SYS user.
Second, issue the SHUTDOWN IMMEDIATE command to shut down the database:
shutdown immediate;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the output:
Database closed.
Database dismounted.
ORACLE instance shut down.Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Third, start the database instance at the OPEN stage:
startupCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the output:
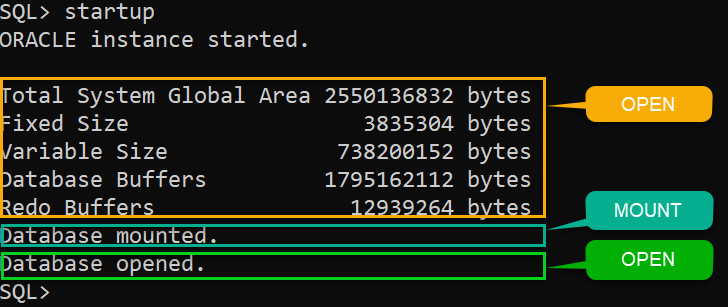
Fourth, shut down the instance again:
shutdown immediate;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Fifth, start the database instance at the MOUNT state:
startup mount;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The output is:
ORACLE instance started.
Total System Global Area 2550136832 bytes
Fixed Size 3835304 bytes
Variable Size 738200152 bytes
Database Buffers 1795162112 bytes
Redo Buffers 12939264 bytes
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Sixth, check the current status of the database instance by querying the v$instance view:
SELECT
instance_name,
status
FROM
v$instance;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
INSTANCE_NAME STATUS
---------------- ------------
orcl MOUNTED
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Seventh, bring the database to the OPEN stage by using the ALTER DATABASE command:
ALTER DATABASE OPEN;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
Database altered.Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Finally, check the status of the database by executing the following statement:
SELECT
instance_name,
status
FROM
v$instance;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Now, the database is open and available for normal operations.
INSTANCE_NAME STATUS
---------------- ------------
orcl OPEN
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this tutorial, you have learned how to start a database instance using the Oracle STARTUP command.