Summary: In this tutorial, you will learn how to use the Oracle CREATE TABLESPACE statement to create a new tablespace in a database.
Introduction to the CREATE TABLESPACE statement #
The CREATE TABLESPACE statement allows you to create a new tablespace.
The following statement shows how to create a new tablespace calledtbs1 with the size of 1MB:
CREATE TABLESPACE tbs
DATAFILE 'tbs_data.dbf'
SIZE 10m;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this statement:
- First, specify the name of the tablespace after the
CREATE TABLESPACEkeywords. In this example, the tablespace name istbs1. - Second, specify the path to the data file of the tablespace in the
DATAFILEclause. In this case, it istbs1.dbf. Note that you can use the datafile full path. - Third, specify the size of the tablespace in the
SIZEclause. In this example,10mstands for10MB, which is relatively small.
On Oracle 23ai or later, when you create a new tablespace, it defaults to a bigfile tablespace. If you want to create a smallfile tablespace, you need to use the SMALLFILE keyword:
CREATE TABLESPACE tbs_small
DATAFILE 'tbs_small_data.dbf'
SIZE 10m;Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Once the tablespace is created, you can find its information by querying data from the dba_data_files view:
SELECT
tablespace_name,
file_name,
bytes / 1024/ 1024 MB
FROM
dba_data_files;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here are all the tablespaces in the current database:
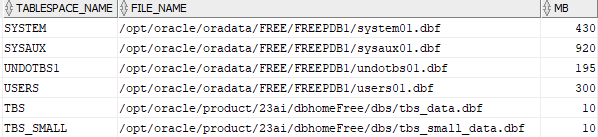
The CREATE TABLESPACE is quite complex with many options, you can find more information from the Oracle CREATE TABLESPACE page.
Tablespaces and the CREATE TABLE statement #
When you create a new table, Oracle automatically places the table in the default tablespace of the user who created the table.
However, you can explicitly specify the tablespace to which the table belongs as shown in the following query:
CREATE TABLE table_name(
...
)
TABLESPACE tablespace_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Note that you must have privileges on the tablespace that you specify in the CREATE TABLE statement. For example:
First, create a new table called t1 whose tablespace is tbs1:
CREATE TABLE t1(
id INT GENERATED ALWAYS AS IDENTITY,
c1 VARCHAR2(32)
) TABLESPACE tbs;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, insert 10,000 rows into the t1 table:
BEGIN
FOR counter IN 1..10000 loop
INSERT INTO t1(c1)
VALUES(sys_guid());
END loop;
END;
/
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Third, check the free space of the tbs1 tablespace by querying from the dba_free_space view:
SELECT
tablespace_name,
bytes / 1024 / 1024 MB
FROM
dba_free_space
WHERE
tablespace_name = 'TBS';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
TABLESPACE_NAME MB
------------------------------ ----------
TBS1 0.9375Code language: CSS (css)Fourth, insert 100,000 rows into the t1 table, Oracle will issue an error due to insufficient storage in the tablespace:
BEGIN
FOR counter IN 1..100000 loop
INSERT INTO t1(c1)
VALUES(sys_guid());
END loop;
END;
/Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the error message:
ORA-01653: unable to increase tablespace TBS by 1MB during insert or update on table OT.T1Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To fix this, you can resize the tablespace using the following ALTER DATABASE statement:
ALTER DATABASE
DATAFILE 'tbs_data.dbf'
RESIZE 10m;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)If you reinsert 100,000 rows into the t1 table, it should work.
The second way to avoid this issue, when creating a new tablespace, you can use the AUTOEXTEND ON clause as follows:
CREATE TABLESPACE tbs1
DATAFILE 'tbs_data.dbf'
SIZE 1m
AUTOEXTEND 200m;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Summary #
- Use the Oracle
CREATE TABLESPACEstatement to create a new tablespace.