Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the Oracle MAX() function to return the maximum value from a set of values.
Oracle MAX() function syntax
The Oracle MAX() function is an aggregate function that returns the maximum value of a set.
The following illustrates the syntax of MAX() function:
MAX( expression );Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Similar to the MIN() function, the DISTINCT and ALL clauses are irrelevant to the MAX() function. The Oracle MAX() function also ignores NULL values.
Oracle MAX() function examples
We will use the products and product_categories tables in the sample database for the demonstration.
A) Simple Oracle MAX() function example
The following example returns the list price of the most expensive (maximum) product:
SELECT
MAX( list_price )
FROM
products;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)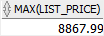
B) Oracle MAX() in subquery
To get the most expensive product information, you use the following query:
SELECT
product_id,
product_name,
list_price
FROM
products
WHERE
list_price =(
SELECT
MAX( list_price )
FROM
products
);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)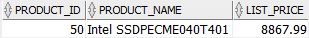
In this example, the subquery returns the highest list price of all products. And the outer query selects the products whose list price is equal to the highest list price.
C) Oracle MAX() with GROUP BY clause
The following statement returns the list price of the most expensive product by product category.
SELECT
category_id,
MAX( list_price )
FROM
products
GROUP BY
category_id
ORDER BY
category_id;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)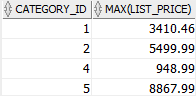
In this example, the GROUP BY clause groups the products by product category (category_id) into subgroups. Then, the MAX() function returns the highest price of products for each group.
Instead of using the category_id, you can use the product category name to make the result set more readable.
To do this, you join the products table with the product_categories table as shown below:
SELECT
category_name,
MAX( list_price )
FROM
products
INNER JOIN product_categories
USING(category_id)
GROUP BY
category_name
ORDER BY
category_name;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)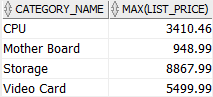
D) Oracle MAX() function with HAVING clause
The following query retrieves the product category and the list prices of the most expensive product per each product category. In addition, it returns only the product category whose highest list price is between 3000 and 5000:
SELECT
category_name,
MAX( list_price )
FROM
products
INNER JOIN product_categories
USING(category_id)
GROUP BY
category_name
HAVING
MAX( list_price ) BETWEEN 3000 AND 6000
ORDER BY
category_name;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)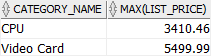
In this example, the HAVING clause specified the condition for filtering the groups.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the Oracle MAX() function to return the maximum value from a set of values.