Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to calculate a cumulative distribution of a value in a set of values by using the Oracle CUME_DIST() function.
Introduction to Oracle CUME_DIST() function
Sometimes, you want to pull the top or bottom x% values from a data set e.g., top 5% salesman by volume. To do this, you can use the Oracle CUME_DIST() function.
The CUME_DIST() function is an analytic function that calculates the cumulative distribution of a value in a set of values. The result of CUME_DIST() is greater than 0 and less than or equal to 1. Tie values evaluate to the same cumulative distribution value.
The following shows the syntax of the Oracle CUME_DIST() function:
CUME_DIST() OVER (
[ query_partition_clause ]
order_by_clause
)
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Because CUME_DIST() function is order sensitive, the order_by_clause is required. The order_by_clause has the following syntax:
ORDER BY expression1
[ASC | DESC ]
[NULLS FIRST | LAST]
[, expression2
[ASC | DESC ]
[NULLS FIRST | LAST],... ]
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The ORDER BY clause specifies the order of rows in each partition.
The query_partition_clause has the following form:
PARTITION BY expression1 [,expression2,..]Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The PARTITION BY clause divides the result set into multiple partitions. It is optional. Omitting this clause means that the function will treat the whole result set as a single partition.
Oracle CUME_DIST() examples
Let’s take some examples of using the Oracle CUME_DIST() function.
Using Oracle CUME_DIST() function over the result set example
The following statement calculates the sales percentile for each salesman in 2017:
SELECT
salesman_id,
sales,
ROUND(cume_dist() OVER (ORDER BY sales DESC) * 100,2) || '%' cume_dist
FROM
salesman_performance
WHERE
YEAR = 2017;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the result:
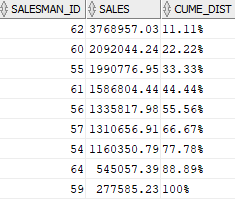
As shown in the output, 33.33 % of salesman have sales amounts greater than 1.99 million.
Using Oracle CUME_DIST() function over partition example
The following statement calculates the sales percentile for each salesman in 2016 and 2017.
SELECT
salesman_id,
year,
sales,
ROUND(CUME_DIST() OVER (
PARTITION BY year
ORDER BY sales DESC
) * 100,2) || '%' cume_dist
FROM
salesman_performance
WHERE
year in (2016,2017);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the output:
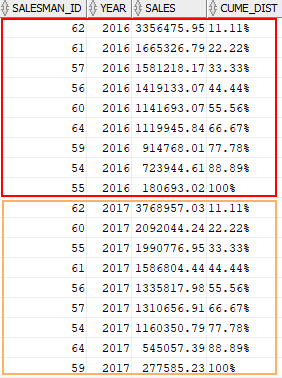
In this example:
- The
PARTITION BYclause divided the result set into two partitions by year, 2016 and 2017. - The
ORDER BYclause sorted rows in each partition by sales amount in descending order to which theCUME_DIST()function is applied.
To get the top 30% of the salesman by sales revenue in 2016 and 2017, you use the following query:
WITH cte_sales AS (
SELECT
salesman_id,
year,
sales,
ROUND(CUME_DIST() OVER (
PARTITION BY year
ORDER BY sales DESC
),2) cume_dist
FROM
salesman_performance
WHERE
year in (2016,2017)
)
SELECT
*
FROM
cte_sales
WHERE
cume_dist <= 0.30;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The output is:
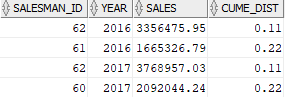
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the Oracle CUME_DIST() function to calculate the cumulative distribution of a value in a set of values.